The Four Phases of Digital Transformation
Discover the Four Phases of Digital Transformation in our latest blog post. Grasp essential concepts, navigate your journey, and take the crucial next step towards business innovation and growth.

As the field of Intelligent Automation (IA) continues to evolve and mature, noticeable patterns surrounding its implementation are coming to light. It has become evident that a successful digital transformation hinges upon the presence of specific program management and technical competencies. These proficiencies encompass aspects such as use case identification, data privacy measures, the total cost of ownership reduction, and more – all of which grow increasingly critical as the IA landscape expands.
We have established a benchmark encompassing four stages of maturity applicable to most organizations. Furthermore, we have identified the programmatic competencies required to support each stage and facilitate a smooth transition through the continuum. However, due to the emergent nature of Intelligent Automation, the path to maturity is not strictly linear. Therefore, as you evaluate the components of each stage, you may discover that certain enablers have been preemptively addressed without a defined understanding of the subsequent steps.
We aim to present a comprehensive, high-level overview of these stages, empowering you to identify gaps and recognize potentially overlooked opportunities throughout the journey.
Risk is necessary. Staying inside the boundaries of what is secure and cozy does not lead to inspiring development. Why not attempt something new when you identify your strengths?
What is Digital Transformation?
Digital Transformation, an enigmatic yet paramount concept, encapsulates the intricate process of harnessing the profound power of cutting-edge technologies to radically re-engineer business operations, revamp customer experiences, and perpetually innovate organizational strategies.
This multifaceted metamorphosis entails not merely the mere implementation of novel digital tools but rather an all-encompassing, sweeping transformation that penetrates the very essence of an enterprise's modus operandi, ultimately fostering an agile, forward-thinking and resilient organizational culture primed to navigate the tumultuous seas of an ever-evolving, hypercompetitive digital landscape.

Early Stage
Analyzing the organization's tools, use cases, and strategic footing; aggressively pursuing proof of concept and pilot projects
Use Case Identification:
Determining the Optimal Starting Point
Most implementations should begin with pinpointing the ideal (or unsuitable) use case, which is the initial step in comprehending how to apply the selected automation tool. This procedure is typically refined multiple times to guarantee the best fit.
Change Management #1
Preparing for the Six Pillars
Implementing Intelligent Automation is viewed as a transformation, which significantly differs from Business As Usual (BAU) change management. As a result, it is crucial to employ supplementary planning and implementation tools to facilitate the smoothest transition possible. The first stage involves assessing the potential of the change.
Operations & IT Strategy
Establishing a Preliminary Infrastructure Platform
In the initial stages of testing the tool's functionality, there is no need for extensive infrastructure investments. Early proofs-of-concept and pilot programs typically do not necessitate substantial installations upfront. Instead, the objective is to support the production load for a few use cases to evaluate what is required for future scaling.
Automation Delivery Methodology #1
Selecting the Appropriate Delivery Method
Although we advise organizations to concentrate on implementing Agile and Scrum methodologies for long-term project delivery, early delivery methods usually adopt a Waterfall approach. Unfortunately, despite being the most prevalent project management style for enterprise software delivery, Waterfall tends to prolong automation timelines and yield substandard products. Consequently, we recommend investigating various methodologies and delivery centers at this juncture to prepare for the journey ahead.
Mid Stage
At least one use case is now being actively produced.
Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) #1:
Determining the preliminary costs and benefits of your initiative
Your initial use cases will assist you in estimating high-level costs during the first year of your program. After completing the Book of Work planning, this procedure will be expanded and refined.
Lean #1:
Fundamentals of Optimization and gap evaluation
Intelligent Automation (IA) implies that business processes are automated by simulating human actions through the application user interfaces they employ. This offers unique possibilities for you to optimize these processes before automating them. The Lean Program imparts a basic comprehension of best practices for reengineering processes before automation.
Book of Work Planning:
Expanding across multiple businesses and timelines
Initial use case identification has its limitations in realizing your vision. To reap the enterprise-grade benefits of IA, you must carry out a large-scale book of work modeling across multiple businesses and/or timelines. This will grant insight into your pipeline and be a primary input for your second-stage CBA exercise.
Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) #2:
Selecting the appropriate delivery approach
The waterfall is the most common early delivery methodology. However, we suggest you investigate different methods at this stage to prepare for future challenges.
Automation Delivery Methodology #2 or #3:
Establishing your factory or enhancing your Center of Excellence (CoE)
Whether your company has a mature Center of Excellence (CoE) framework (#2) or you are establishing a factory for the first time (#3), this phase transitions your methodology from the tactical program and project management to decision-making regarding delivery and centralization.
Growth Stage
Multiple unrelated use cases are currently being implemented, and there is a lack of enterprise cohesiveness.
Lean Initiative #2
Enhancing Process Improvement Approaches within Your IA Framework
The Lean Practitioner Program provides essential guidance for organizations lacking a formal Lean structure or those seeking to supplement their current methods with an optimization strategy tailored specifically for IA.
Power User Program Initiative #1
Evaluating Scalability and Cost Reduction Strategies
As your organization expands, the total cost of ownership can decrease substantially over time. However, this requires harnessing the tool's configurability by non-technical staff, citizen developers, or Power Users. Therefore, identifying these individuals early on is crucial.
IT Scaling
Broadening Infrastructure to Accommodate Growing Production Demands
Initiating the construction of suitable infrastructure can commence as early as the Mid-Stage, but it is frequently more effective during the Growth Stage. At this juncture, your experience enables informed decisions that significantly affect costs, such as choosing between on-premise and cloud solutions.
Change Management Initiative #2
Preparing the Organization for Transformation
Embracing the full potential of Intelligent Automation will fundamentally alter your business operations, impacting every aspect of the company, its customers, and employees. This stage is typically when your Change Management plans are poised for implementation.
Power User Program Initiative #2
Establishing the Advanced Factory or CoE 2.0
Transitioning developers and power users becomes a priority towards the latter part of the Growth Stage. This shift may occur sooner as IA best practices gain traction in the market. First, however, it is vital to address any issues before deploying this technology as an end-user computing tool (EUC).
Mature Stage
Integrated, scalable, and centralized program
Portfolio Management Excellence Strategies
Transitioning from Key Performance Indicators to Comprehensive Business Insights
As your program matures, substantial refinements, adjustments, and digital transformations will take place on a scale demanding the application of organization-wide intelligence. Therefore, we advise proactively standardizing dashboards for integration with expansive big data visualizations and reporting.
Modernizing Information Technology Infrastructure
Adopting Cutting-Edge Innovations
As the technological landscape evolves, so do the available resources for Intelligent Automation (IA) support. At this juncture, your organization may transition to a cloud-based platform or even explore IA as a service.
Proactive Thought Leadership
Tapping into Your Network for Novel Perspectives
Upon reaching maturity, your business is primed for significant scaling. This signifies a readiness for your organization to excel in novel ways. Seize this opportunity to engage with a more experienced network, capitalizing on the best practices of industry leaders. Adopting a tried-and-tested approach or utilizing it to validate your strategy is an essential final step in evolving into an IA Business-as-Usual (BAU) Enterprise.
Conclusion
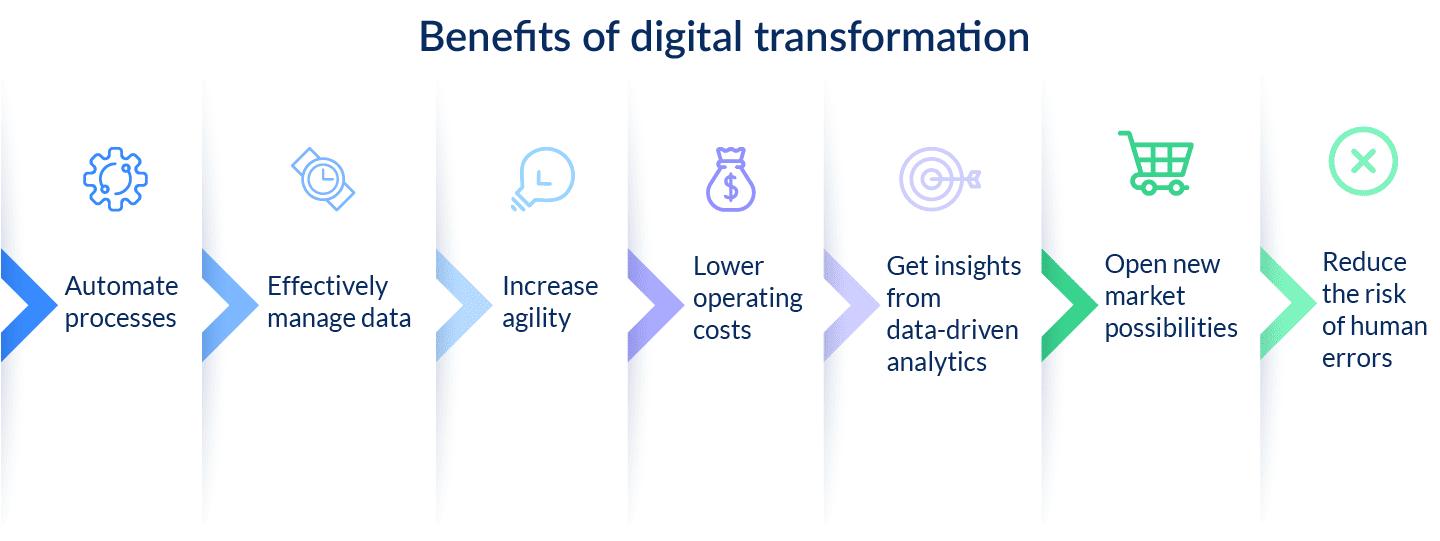
By wholeheartedly adopting digital transformation, businesses have the potential to enhance their operational performance, elevate their efficacy, curtail expenses, generate innovative products and services, and penetrate fresh market territories.
- Elevate customer experience: Utilizing digital transformation, corporations can elevate customer experiences in many ways. For instance, businesses can employ digital solutions to offer clients bespoke service, facilitate seamless interactions, and supply comprehensive information regarding their offerings.
- Augment efficiency: Through digital transformation, organizations can bolster efficiency in numerous ways. As an example, businesses can integrate digital tools to automate tasks, refine processes, and foster seamless collaboration among team members.
- Minimize expenses: By leveraging digital transformation, enterprises can diminish costs in various manners. For example, companies can harness digital innovations to decrease paper consumption, automate operations, and delegate non-essential functions to external sources.
- Innovate products and services: Digital transformation paves the way for creating novel products and services. Companies can utilize cutting-edge digital technologies to engineer new software solutions, establish unique online platforms, and initiate innovative marketing initiatives.
- Venture into emerging markets: Digital transformation enables businesses to explore untapped markets. Corporations can employ digital strategies to connect with novel customer segments, broaden distribution networks, and introduce offerings to new geographic locations.
Pioneering Examples
-
Global E-Commerce Expansion: Amazon's meteoric rise from an online bookstore to a worldwide e-commerce giant demonstrates the power of digital transformation. By leveraging advanced algorithms, artificial intelligence, and data analytics, Amazon has revolutionized customer experiences and supply chain management.
-
Ride-Hailing Revolution: Uber and Lyft have embraced digital technologies by disrupting the traditional taxi industry. Their innovative platforms connect riders with drivers through mobile apps, creating seamless, convenient transportation experiences and reshaping urban mobility.
-
Streaming Media Dominance: Netflix and Spotify have transformed the entertainment landscape with their digital-first approach. These platforms have altered consumption patterns and user expectations by offering vast content libraries, personalized recommendations, and on-demand access.
-
Remote Work Reinvention: Slack, Zoom, and Microsoft Teams have capitalized on digital transformation by enabling remote work and fostering virtual collaboration. By leveraging cloud-based communication tools, these companies have reshaped the modern workplace and increased operational flexibility.
-
Telemedicine Advancements: Healthcare providers like Teladoc and Amwell have utilized digital technology to improve patient access to care. These organizations are driving the future of healthcare by offering virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and AI-powered diagnostics.
-
Smart City Innovations: Cities like Barcelona and Singapore have adopted digital transformation to enhance urban living worldwide. These smart cities optimize resource management, transportation, and public safety by integrating IoT devices, data analytics, and AI-powered solutions.
-
Personal Finance Disruption: FinTech companies like Square and Robinhood have democratized financial services through digital transformation. These innovators have expanded access to payment processing, investing, and other financial tools by offering user-friendly, mobile-first platforms.
Let's talk
If you have any questions about digital transformation, don't hesitate to contact us. We would be happy to answer any questions and help you get started.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help digitally transform your business.